|
|
|
|
|
|
|
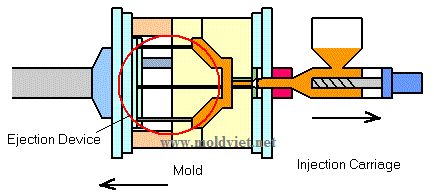
(1) Melt the material in the barrel. |
(2) Inject the material into the mold. |
(3) Cool down and remove the part. |
|
This chapter explains the process, advantages and disadvantages
as well as the operation of an injection mold.
|
Injection molding is one of the major methods for plastics molding. This method is widely used for various molded products because it is possible to produce parts of high quality at a low cost and in a short time.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1) Melt the material in the barrel. |
(2) Inject the material into the mold. |
(3) Cool down and remove the part. |
Now, let's learn more in detail about the movement and the role of injection molding using a screw type injection molding machine.
|
|
Closing mold, Clamping mold
|
If a mold is closed too quickly, the mold may be deformed; therefore, clamping
the mold involves two steps.
Two-step mold clamping also helps to prevent foreign matter that is sometimes
left behind in the mold from damaging or destroying the mold if the clamping
of the mold is done by high pressure.

|
|
Injection Nozzle Seating, Injection |
The pressure used to inject the molten plastics to the mold is called the primary
pressure.

|
|
Holding pressure, Cooling, Plastication
|
Even after the molten plastics is injected into the mold, the holding pressure
is maintained while the molten plastics cools in the mold.
While the molten plastics is being cooled and solidified
in the mold, the molten material for the next molding will be plasticated.
This plastication is done by the heat generated in mixing the resin with
a screw, or the band heater that is attached around the heated barrel.
Holding pressure is also called the secondary pressure. It is used to add
more molten plastics by putting pressure on the filled molten plastics in
the mold for mold shrinkage that is
caused by cooling solidification, so that the sink mark
of parts can be reduced.

Å@
|
|
Injection nozzle removal, mold opening,
part removal
|